How To Register An Instance Of A Class With An Instance Of An Observer Class
🤖📘🍻 Hooray! After iii years of work, we've finally released a new ebook on pattern patterns! Check it out »
Observer Design Pattern
Intent
- Define a i-to-many dependency betwixt objects so that when 1 object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
- Encapsulate the core (or common or engine) components in a Subject abstraction, and the variable (or optional or user interface) components in an Observer hierarchy.
- The "View" part of Model-View-Controller.
Problem
A large monolithic design does non scale well as new graphing or monitoring requirements are levied.
Discussion
Ascertain an object that is the "keeper" of the information model and/or concern logic (the Bailiwick). Delegate all "view" functionality to decoupled and singled-out Observer objects. Observers register themselves with the Subject equally they are created. Whenever the Subject field changes, it broadcasts to all registered Observers that it has changed, and each Observer queries the Subject area for that subset of the Subject's state that it is responsible for monitoring.
This allows the number and "type" of "view" objects to be configured dynamically, instead of being statically specified at compile-fourth dimension.
The protocol described higher up specifies a "pull" interaction model. Instead of the Subject "pushing" what has changed to all Observers, each Observer is responsible for "pulling" its particular "window of interest" from the Field of study. The "push" model compromises reuse, while the "pull" model is less efficient.
Issues that are discussed, but left to the discretion of the designer, include: implementing upshot compression (merely sending a unmarried change broadcast after a series of consecutive changes has occurred), having a single Observer monitoring multiple Subjects, and ensuring that a Bailiwick notify its Observers when it is nigh to go abroad.
The Observer blueprint captures the panthera leo's share of the Model-View-Controller architecture that has been a part of the Smalltalk community for years.
Structure
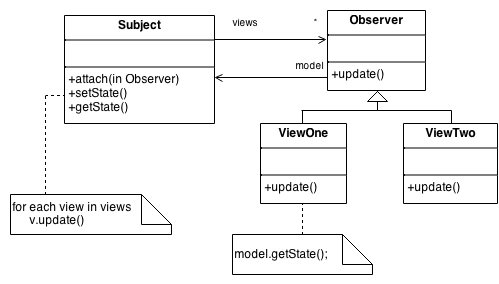
Subject represents the core (or independent or common or engine) abstraction. Observer represents the variable (or dependent or optional or user interface) abstraction. The Field of study prompts the Observer objects to practise their thing. Each Observer tin think to the Bailiwick as needed.
Instance
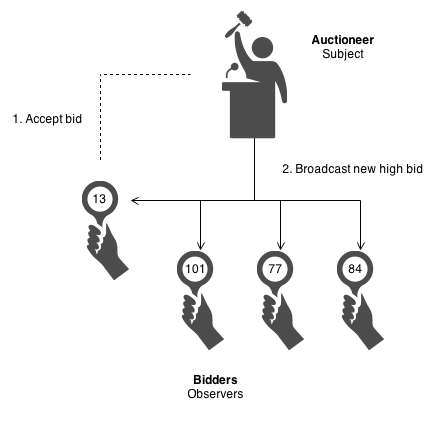
The Observer defines a one-to-many relationship then that when one object changes country, the others are notified and updated automatically. Some auctions demonstrate this blueprint. Each bidder possesses a numbered paddle that is used to signal a bid. The auctioneer starts the bidding, and "observes" when a paddle is raised to accept the bid. The acceptance of the bid changes the bid toll which is broadcast to all of the bidders in the form of a new bid.
Check list
- Differentiate between the core (or independent) functionality and the optional (or dependent) functionality.
- Model the independent functionality with a "subject field" abstraction.
- Model the dependent functionality with an "observer" hierarchy.
- The Subject field is coupled simply to the Observer base of operations class.
- The client configures the number and type of Observers.
- Observers annals themselves with the Subject.
- The Subject field broadcasts events to all registered Observers.
- The Subject may "push" information at the Observers, or, the Observers may "pull" the information they need from the Subject.
Rules of thumb
- Chain of Responsibility, Command, Mediator, and Observer, address how y'all can decouple senders and receivers, just with different merchandise-offs. Concatenation of Responsibility passes a sender asking along a chain of potential receivers. Command unremarkably specifies a sender-receiver connection with a subclass. Mediator has senders and receivers reference each other indirectly. Observer defines a very decoupled interface that allows for multiple receivers to exist configured at run-fourth dimension.
- Mediator and Observer are competing patterns. The departure betwixt them is that Observer distributes communication by introducing "observer" and "subject" objects, whereas a Mediator object encapsulates the communication betwixt other objects. We've plant information technology easier to make reusable Observers and Subjects than to make reusable Mediators.
- On the other paw, Mediator tin can leverage Observer for dynamically registering colleagues and communicating with them.
Code examples
More than info, diagrams and examples of the Observer pattern blueprint you can detect on our new partner resource Refactoring.Guru.
Source: https://sourcemaking.com/design_patterns/observer
Posted by: behanworturearown.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Register An Instance Of A Class With An Instance Of An Observer Class"
Post a Comment